Cholesteatoma Of Attic Definition
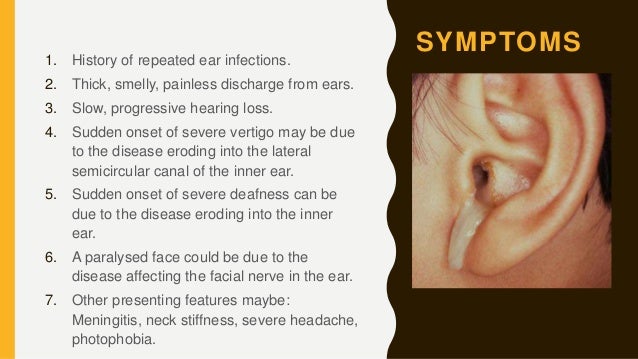
Often presents with a malodorous ear discharge with associated hearing loss.
Cholesteatoma of attic definition. It may be a birth defect but it s most commonly caused by repeated. Medical definition of cholesteatoma. They often become infected and can result in chronically draining ears. A cholesteatoma is a skin growth in your middle ear behind your eardrum.
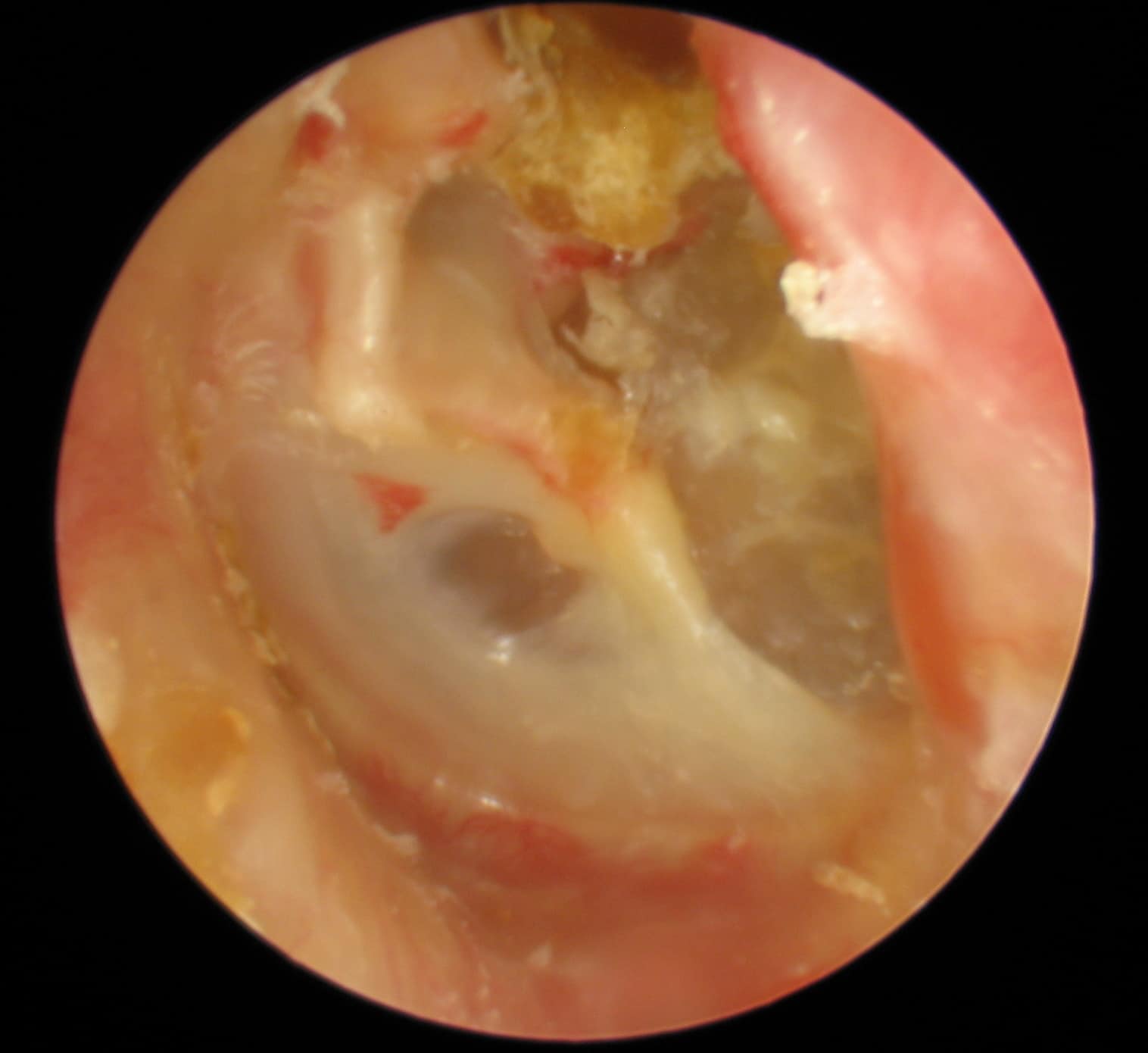
Invagination of the tympanic membrane of the attic to form retraction pockets to be filled with desquamated epithelium and keratin to form cholesteatoma. Diagnosis is clinical based on history and otoscopic findings. As skin cells gather the cholesteatoma grows. A cholesteatoma is an abnormal noncancerous skin growth that can develop in the middle section of your ear behind the eardrum.
Cholesteatoma is an accumulation of squamous epithelium and keratin debris that usually involves the middle ear and mastoid. Cholesteatoma is a destructive and expanding growth consisting of keratinizing squamous epithelium in the middle ear and or mastoid process. This can result in the destruction of the bones of the middle ear as well as growth through the base of the skull into the brain. Wikipedia lexilogos oxford cambridge chambers harrap wordreference collins lexibase dictionaries merriam webster.
Dr subhan iqbal and assoc prof frank gaillard et al. You can complete the definition of attic cholesteatoma given by the english cobuild dictionary with other english dictionaries. A large epitympanic attic cholesteatoma that is much more advanced than the lesion in the previous image. Search attic cholesteatoma and thousands of other words in english cobuild dictionary from reverso.
Eustachian tube theory. No landmarks are visible which typically is the case with. Although benign it may enlarge and invade adjacent bone. Cholesteatomas are not cancerous as the name may suggest but can cause significant problems because of their erosive and expansile properties.
Squamous metaplasia or extension of squamous cell epithelium inward to line an expanding cystic cavity that may involve the middle ear or mastoid erode surrounding bone and become filled with a mass of keratinized squamous cell epithelial debris usually resulting from chronic otitis media. An epidermoid cyst usually in the brain arising from aberrant embryonic rests and appearing as a compact shiny flaky mass called also pearly tumor. Cholesteatomas are histologically equivalent to an epidermoid cyst and are composed of desquamated keratinizing stratified squamous epithelium forming a mass.