Coefficient Of Kinetic Friction Of Sheet Metal

In the micro sheet metal roll forming process the kinetic friction is significant indicating the real contact area is affected by the junction growth effect according to brizmer et al.
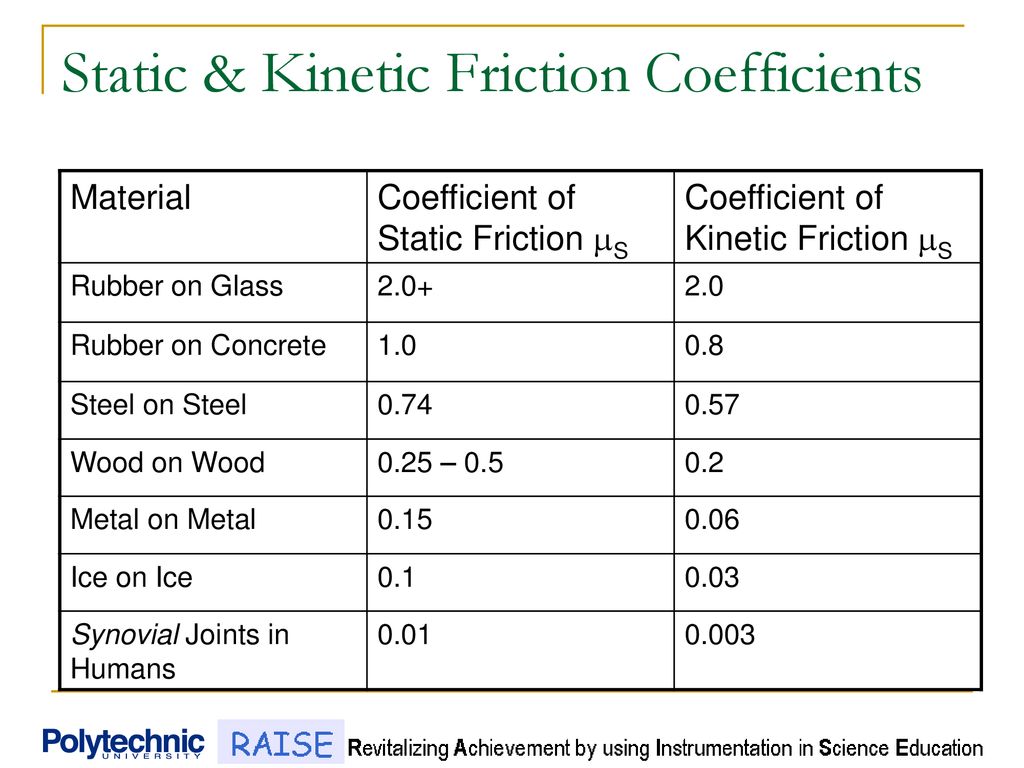
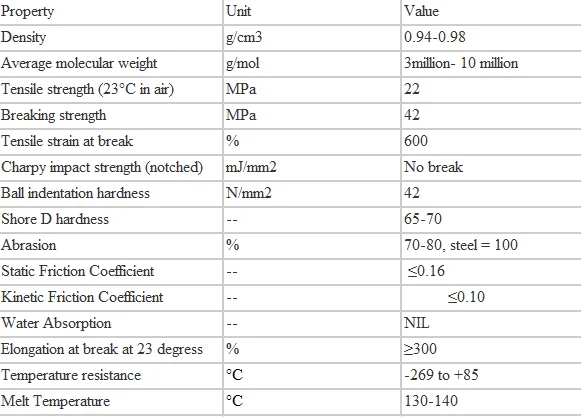
Coefficient of kinetic friction of sheet metal. Typically steel on steel dry static friction coefficient 0 8 drops to 0 4 when sliding is initiated and steel on steel lubricated static friction coefficient 0 16 drops to 0 04 when sliding is initiated. Coefficient of friction friction force develops between contacting surfaces of two bodies and acts to resist relative motion between the bodies. To cause motion you need to slightly increase m the hanging mass by 0 1 gram for example. The coefficient of kinetic friction is denoted by the greek letter mu μ with a subscript k.
Since friction is a force the unit of the frictional force is the newton n. Assuming purely plastic real contacts newton s law of viscosity and a square root behavior of the hydrodynamic coefficient of friction with respect to the hydrodynamic hersey parameter an analytic model is found. The coefficient of kinetic friction is the ratio f w or mg mg or simply m m. Based on the data you enter if the ratio m m is exactly equal to the selected μ no motion will occur.
This paper presents the derivation of a first order friction model for lubricated sheet metal forming. The frictional force for static friction can be expressed as. The kinetic friction equation can be written as. Hence the real contact area must be recalculated for the accurate description of friction behavior.
It should be noted that there can be significant differences between static friction typically higher and kinetic sliding friction. The force of kinetic friction is μk times the normal force on a body. Where μsis the coefficient of static friction and μkis the coefficient of kinetic friction. F max μ f n.
The friction coefficients considered below are for static friction cases where two solid surfaces in contact with each other are resisting relative lateral motion. It is expressed in newtons n. Sorry to see that you are blocking ads on the engineering toolbox. Where f k is the force of kinetic friction μ k is the coefficient of sliding friction or kinetic friction and f n is the normal force equal to the object s weight if the problem involves a horizontal surface and no other vertical forces are acting i e f n mg where m is the object s mass and g is the acceleration due to gravity.
The value of μsis generally higher than the value of μkfor a given combination of materials.